Sugar
Know About Raw Sugar Manufacturing Process
In this sugar article discussed about raw sugar definition, basic steps for raw sugar making process and raw sugar specifications.What is Raw Sugar:
Raw Sugar is producing from sugar cane or beet by ordinary process known as Defecation process. According to Peter Rein raw sugar can be defined as “Brown sugar produced in a raw sugar mill generally destined for further processing to refined sugar”.
a) It is Unwashed centrifugal sugar with minimum polarization 96.5o .
b) Raw sugar surrounded by the original film of molasses, to be further refined or reprocessed for making it direct consumption sugar.
Flow Chart of Raw Sugar Process
The main steps in raw sugar making process:
Juice Extraction
The following technologies are using the extraction of juice from sugar cane or sugar beet
Milling Technology
In this process follow four or five stages (set of mills) for juice extraction in milling process. According to that the set of mills the system is called as 5-Milling Tandem or 4-Milling Tandem.
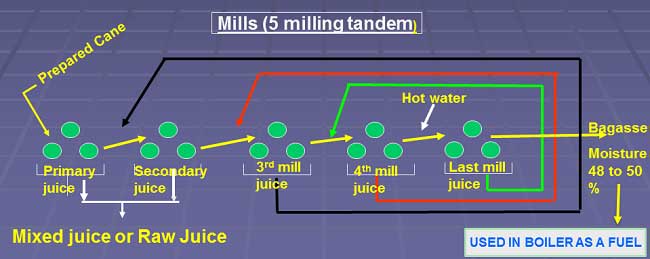
The milling tandem hot water is used for maximum extraction of juice from prepared cane. This hot water is also called imbibition water.
Mill sanitation
The first important operation in the Raw sugar manufacture is the “sanitation”. Every unit from mills to conveyors is kept clean to prevent the bacterial infection. To control the growth of dextran the good quality mill sanitation chemicals should be used in optimum dose. The growth of dextran should be controlled through proper sanitation.
Diffusion Technology
In the Diffusion process, sugar extraction from cane or sugar beet is actually effected by rupturing the cell of the prepared cane or beet cell and then washing the ruptured cells with hot water or low concentrated juice obtained in the same process.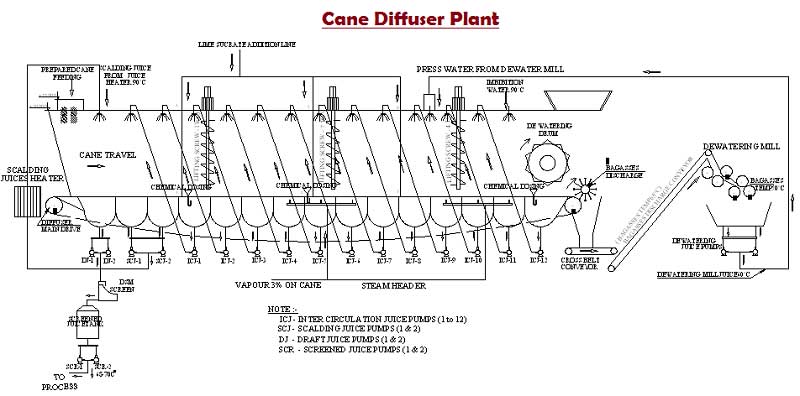
Defecation Process
The process of Defecation is used in the clarification process of raw sugar and also Organic sugar manufacturing industry.
After extraction of the juice from sugar cane by milling or diffuser technology is subjected to defecation process. This process can be defined as a neutralize the raw juice by adding of lime (add in the form of Milk of lime).
a) This is the oldest & cheapest method of juice clarification
b) In this process lime & heat are two basic agents.
c) The lime and heat treatment forms a heavy precipitate of complex composition.
d) Contains in soluble lime salts, coagulated albumin, and varying proportion of the fats, waxes and gums.
e) Phosphoric acid is added to increase P2O5 content of juice to 300 ppm.
f) Then lime added to neutralize organic acids,
d) Besides insoluble tricalcium phosphate [Ca3 (PO4) 2] is also formed which occludes colloids & suspended impurities.
For more information regarding the Defication process please go through the below linkConcepts of Juice Defecation Process in Raw Sugar Manufacturing Process
SettlingThe limed juice or deficated juice or treated juice is heated up to 1020 C to 1030 C and then sent to clarifier for settling & further filtration purpose.
The function of juice clarifier is to separate insoluble solids in limed juice (Deficated juice), which are in “flocs” by means of settling and allowing the clear Juice.
The settling process separates the treated juices treated into two layers of clear juice which rises to the top surface and mud which collects at the bottom of the clarifer.
The different types of clarifier design to carryout this separation as completely and rapidly as possible. Normally settling aid is added so as to maintain the juice free from suspended matter and turbidity.
The settled mud in clarifier contains also having sugar so it will be extracted by using vacuum filters or decanters technology. The extracted juice in vacuum filters is again sent back to the defication process.
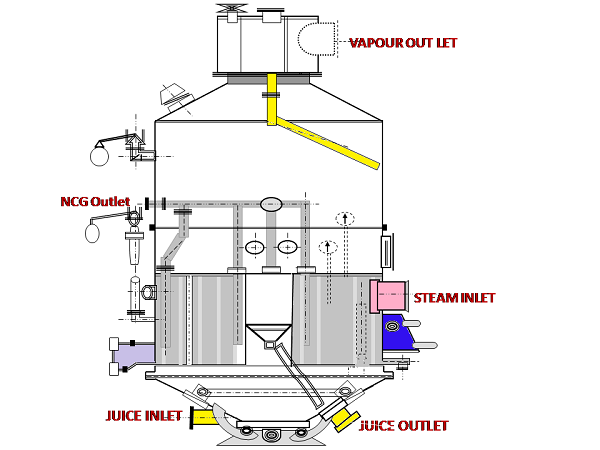
Evaporation
The clarified juice sent to evaporator bodies to increase its solid concentration. After evaporation it is called as a syrup.
In the process of evaporation, the concentration of clear juice is carried out until the percentage of solids has reached upto 60% 70% as per the requirement. This evaporation process is conducted under a system of multiple effect evaporators as per the view of energy conservation.
Crystallization
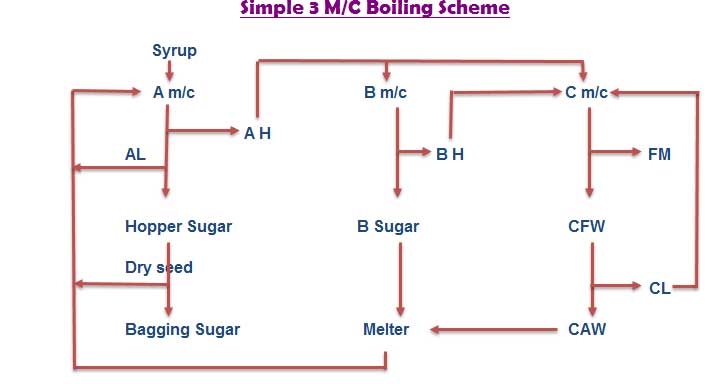
The concentrated juice means syrup is subjected to process of crystallization. In the crystallization process consists of concentration of syrup and formation of sugar crystal. This process is done by vacuum pans.
Straight there massecuite boiling scheme is followed for raw sugar making has to be taken to ensure uniformity and proper size of sugar grains. The raw sugar crystals are surrendered by thin film of molasses and thus having brownish appearance.
 The massecuite produced from vacuum pans is dropped to cylindrical or ‘U’ shaped vessel equipped with slow speed stirring element which is called as a crystalliser.
The massecuite produced from vacuum pans is dropped to cylindrical or ‘U’ shaped vessel equipped with slow speed stirring element which is called as a crystalliser.
Centrifuging and Drying
The massecuite from crystallizers is taken into centrifugals to for the separation of sugar crystals and molasses. The centrifugal machine in which crystals in the massecuite are separated by using centrifugal force from the surrounding molasses or syrup.
In raw sugar production, use little bit of washing of ” A massecuite” sugar in the Centrifugal and it is to be followed as per the output raw sugar colour requirement. After centrifuging, the raw sugar dying flowed by cooling on hopper by blowing hot and cold air. Bagging temp should be maintained near to room temperature to prevent caking of raw sugar. The raw sugar should be quickly moved to refined sugar process as far as possible or otherwise to be stored in humid proof godown.
Specifications of Raw Sugar |
||
| Sr.No. | Characteristic | Requirement |
| 1 | POL ( min in %) | 95.6 |
| 2 | R.S. by mass ( max in %) | 1 |
| 3 | Sulphited ash % by mass (max %) | 0.8 |
| 3 | Ash % by mass ( max in %) | 0.8 |
| 4 | Safety factor ( min in %) | 0.3 |
| 5 | Crystal size ( material to be retain on 0.5mm IS sieve %) | 95 |
| 6 | Sulphur dioxide ( max in ppm) | 20 |
Specifications of VHP (Very High Pol) Raw Sugar |
||
| Sr.No. | Characteristic | Requirement |
| 1 | POL ( min in %) | 99.0 to 99.5 |
| 2 | Moisture (Max in %) | 0.08 to 0.15 |
| 3 | R.S. by mass ( max in %) | 0.1 to 0.12 |
| 4 | Ash % by mass ( max in %) | 0.1 to 0.13 |
| 5 | Colour in ICUMSA | 800 to 1200 IU |
| 6 | Starch ( max in ppm) | 200 to 250 |
| 7 | Dextran ( max in ppm) | 100 to 150 |

